|
PinkMonkey Online Study Guide-Biology
2.4 Lipids
Fats and their derivatives are collectively called lipids.
Fats are compounds containing fatty acids and glycerol. They are
composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, but less oxygen than that
in carbohydrates. Fatty acids are long chains of CH2
groups with terminal methyl and carboxyl groups with general formula
CH3[CH2]n-COOH, while glycerol molecule contains
a chain of three carbon atoms and has a formula C3H6O3.
In the formation of fat, three molecules of fatty acids are combined
with three-OH groups on one molecule of glycerol, with removal of
3 molecules of water which is represented as follows :
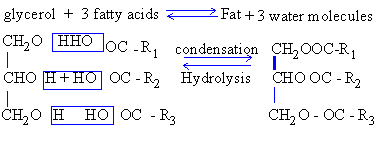
Formation of Fat molecule
There are mainly three types of lipids . the simple lipids,
commonly known as fats and oils, the compound lipids such as phospholipids
and glycolipids which on hydrolysis yield not only alcohol and fatty acids
but also other compounds and derived lipids such as steroids which include
cholesterol, Vitamin D, estrogen , testosterone, cortisol, etc. Lipids
are practically insoluble in water but are soluble in organic solvents
like chloroform, ether and benzene.
Fats stored in cells are usually clear oil droplets called
globules. Because fats do not dissolve in water, animals store fat in
large clear globules in the cells of adipose tissue. The enzyme lipose
breaks down fats into fatty acids and glycerol which can be furthur broken
down to produce energy.
*********
|
Table of Contents
2.0 - Introduction
2.1 Structural Organization and Chemical Basis Of Life
2.2 Organic Compounds
2.3 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acid
2.4 Lipids
Chapter 3
|