|
PinkMonkey Online Study Guide-Biology
2.2 Organic Compounds
Many chemical compounds in living organisms are known
as organic compounds' which contain C,H and O. In the earlier chapter
we have seen that an organism is formed primarily from six elements: C,
H, O, N, P, Ca. The study of organic compounds is called organic chemistry.
(A) Carbohydrates
There are plenty of organic compounds present
in nature. All living things contain basically four types of organic
compounds.Carbohydrates form the first category of organic compounds.
For metabolism the organism requires energy. This energy
is provided primarily by carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are basically composed
of 3 elements, C, H, and O. The ratio of H to O is 2:1, as in a water
molecule (H2O). There are types of carbohydrates according
to the complexity of the carbohydrate molecule. Carbohydrates and usually
taste sweet to humans are referred to as sugar. If a carbohydrate is made
up from a single molecule it is called monosaccharide. When the
carbohydrate is made up of 2 sugar molecules linked together it is referred
to as a adisaccharide Carbohydrates which have more than 3 molecules
are called polysaccharides. The general formula to represent the
carbohydrate is Cx(H2O)y.
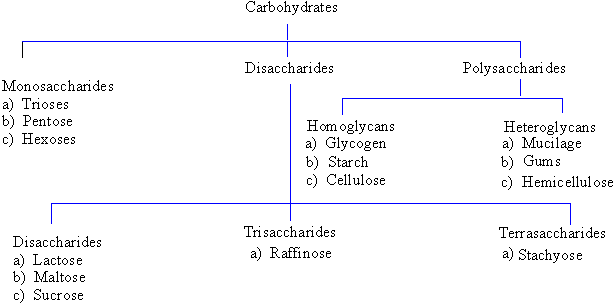
Click here to enlarge
Table I : Schematic Representation of Carbohydrates
1) Monosaccharides
They are the simplest soluble sugar. Depending
on the number of carbon atoms present, monosaccharides are further
classified as:
a) trioses ® (3
carbons) C3H6O3 e.g. glyceraldehyde b) pentoses ®
(5 carbons) C5H10O5 e.g.
ribose and deoxyribose
c) hexoses ® (6
carbons) C6H12O6 e.g. glucose
Glucose C6H12O6 is a
basic form of fuel in all living things. It is soluble in blood plasma
and water and so it is transported by body fluids to all cells in the
body. In cells it is metabolized and releases energy. Glucose is also
the main product of photosynthesis and also an initiating material for
cellular respiration.
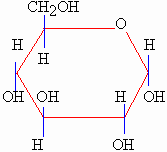
Figure 2.2 A molecular representation of glucose
|