|
16.5 Lenses
Note :
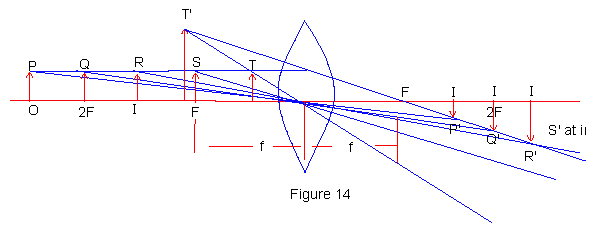
(1) The ray diagrams are drawn conventionally, i.e. the incident ray penetrates the lens till central part of lens is undeviated. The effect of refraction then is in such a way that the ray parallel to axis will pass or appear to pass through the focus. (2) The ray that is incident through the centre of lens is undeviated as it goes out of the lens.
The image formations for various positions of objects are shown in Fig. 14
in case of bi-convex lens.
For any position of object OP, the image IP formed is always between F & M (centre of lens), as illustrated in
|
16.1
Laws of Reflection at plane surfaces Follow @Pinkmonkey_com  |