|
Also,  which is the instantaneous velocity of the body at time ‘t’. which is the instantaneous velocity of the body at time ‘t’.
Example 10
Find the gradient of the curve y = 2 x2
- 6 x at (2 , 4 ) from the first principle.
1) y = f (x) = 2 x2 -
6 x
2) y + D
y = f ( x + D
x ) = 2 ( x + D
x ) 2 -
6 ( x + D x )
Subtracting
D y = 2
x2 + 4 x D
x + 2 ( D
x )2 -
6 x - 6
D x - 2 x2 + 6 x
= 4 x D
x + 2 (D
x)2 -
6 D x
3) \ 
= 4 x + 2 D
x - 6
4) \ 
= ( 4 x
+ 2 D x - 6 )
= 4 x + 2 (
0 ) - 6
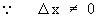

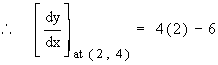
= 2
\ The gradient at ( 2 , 4 ) is 2.
Example 11
Differentiate y = Öx w . r. to
x, from the first principle.
1) y = Öx
\ y +
D y = 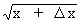
2) Subtracting
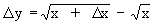
|