|
REMARK: (1) Progressive and Regressive derivatives
The progressive derivative of ‘f ’ at x = a is
given by 
 , h > 0 i.e. h ® 0+
or x ® a+
and it is denoted by R f ’ ( a ) or by f ’(a + 0) or by f ’ ( a+)
. It is also known as the Right hand derivative of ‘f ’ at x = a.
, h > 0 i.e. h ® 0+
or x ® a+
and it is denoted by R f ’ ( a ) or by f ’(a + 0) or by f ’ ( a+)
. It is also known as the Right hand derivative of ‘f ’ at x = a.
The regressive derivative of ’ f ’ at x = a, is given by

 , h > 0 i.e. h ®
0-or x ® a-
and it is denoted by Lf ’ (a) or by f ’ ( a - 0) or f " (a-
). It is also know as the Left hand derivative of ‘ f ’ at x = a
, h > 0 i.e. h ®
0-or x ® a-
and it is denoted by Lf ’ (a) or by f ’ ( a - 0) or f " (a-
). It is also know as the Left hand derivative of ‘ f ’ at x = a
It is easy to see that f ’ (a) exists if and only if Rf ’ (a) and Lf ’ (a) exist and are equal.
Example 1
Consider the derivability of the function f(x) = | x | at the origin.
Left hand derivative = 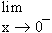 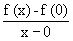
= 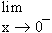 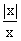
= 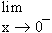 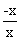
= -1
Right hand derivative = 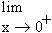
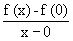
= 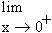 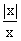
= 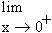 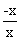
= +1
Thus f ’ (0 - ) ¹ f ’ (0
+ ). Hence the function is not derivable at x = 0
|