|
PinkMonkey Online Study Guide-Biology
8. 3 Replication Of DNA In Eukaryotes
Definition: "The process by which DNA produces
daughter DNA molecules which are exact copies of the original DNA is called
replication of DNA."
In eukaryotes, DNA is double stranded. The two strands
are complementary to each other because of their base sequences.
Semi-conservative method of DNA replication
Important points:
(i) This is the most common method of DNA replication.
(ii) It takes place in the nucleus where the DNA is present
in the chromosomes.
(iii) Replication takes place in the S-phase (synthesis phase)
of the interphase nucleus.
(iv) The deoxyribose nucleotides needed for the formation of
the new DNA strands are present in the nucleoplasm.
At the time of replication, the two strands of DNA first
separate. Each strand then acts as a template for the formation
of a new strand. A new strand is constructed on each old strand, and two
exactly identical double stranded DNA molecules are formed. In each new
DNA molecule, one strand is old (original) while the other is
newly formed. Hence, Watson and Crick described this method as semi-conservative
replication.
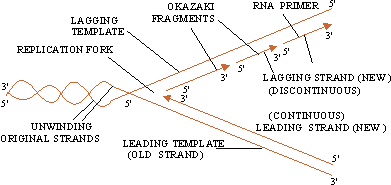 Click here to enlarge
Click here to enlarge
(A) An overall process of DNA replication showing replication fork and formation of new strands template and lagging template
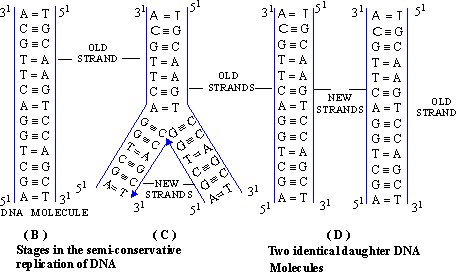 Click here to enlarge
Click here to enlarge
Figure 8.6 Stages in the semi-conservative method of DNA replication in eukaryotes
|