|
PinkMonkey Online Study Guide-Biology
8.2 The Structure of DNA
Deoxyribonucleic nucleic Acid (DNA) is a highly
complex megabiomolecule. The long chain molecule is formed of repeating
units called nucleotides. Hence, it is described as the polynucleotide
molecule. It consists of two polynucleotide antiparallel strands
which are spirally coiled round each other along their lengths (Watson
and Crick, 1953).
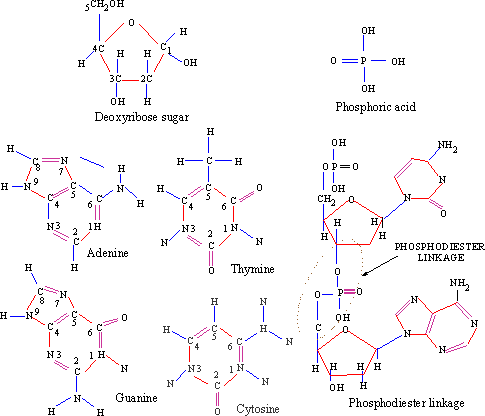
(a) Chemical Components of DNA : The highly complex
DNA molecule is composed of only three types of chemical components. These
are (i) deoxyribose sugar, (ii) a phosphate, and (iii) nitrogen containing
organic bases.
-
Deoxyribose sugar : The sugar present in the
DNA molecule is called deoxyribose sugar and hence the nucleic acid
is called deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). It is a pentose sugar (with
5 carbon atoms) having a pentagonal ring structure (Figure 8.3)
Phosphate (Figure 8.3) : The phosphate in the DNA is present as phosphoric acid (H3PO4). It has three reactive (-OH) groups of which two are involved in the formation of the sugar-phosphate backbone of each DNA strand. -
The nitrogen-containing organic bases

These are heterocyclic compounds containing nitrogen in their
rings and therefore called nitrogenous bases. DNA contains
four different bases called adenine (A), guanine (G)
cytosine (C), and thymine (T). These are grouped into
two classes on the basis of their chemical structure: (i) Purines
(with a double ring structure) and (ii) Pyrimidines (with
a single ring structure) (Figure 8.3)
Nucleosides : In the molecules of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA), each pentose sugar molecule has one nitrogen base attached at carbon number 1. It may be either a purine or a pyrimidine base. Thus, a pentose sugar with the attached N-base forms a nucleoside.
[Sugar + N-base] = Nucleoside.
In DNA, the deoxyribose sugar has one of the four bases (A,G,T or C) attached. Therefore, the nucleosides in DNA are called deoxyribosides.
[deoxyribose sugar + N-base] = Deoxyriboside
 Click here to enlarge
Click here to enlarge
Fig.8.3 Chemical components of DNA and the phosphodiester linkage
Nucleotides : A nucleoside with a phosphate group attached to it is called a nucleotide.
[Nucleoside + Phosphate] = Nucleotide
A nucleotide is the basic unit or monomer in the structure
of a nucleic acid molecule.
Thus, a nucleotide is a nucleoside phosphate. In a nucleotide, the phosphate group is linked with the pentose sugar at carbon-5.
In the DNA, each nucleotide is called deoxyribonucleotide.
[Deoxyribose sugar + N-base + Phosphate] = Deoxyribonucleotide
As there are four different bases (A,#T,#G and C) in
DNA, there can be only four types of nucleotides in DNA.
The nucleotides act as the building block molecules for the synthesis of the polynucleotide molecules. When two nucleotides are linked together, a dinucleotide (or dimer) results.
|