Fermentation is of different types and takes place
under anaerobic conditions mostly in saprophytic microorganisms
like certain bacteria and fungi. However, it may also take place
in higher organisms under certain conditions.
The two most common types of fermentation are (1)
alcoholic fermentation and (2) lactic acid fermentation.
(1) Alcoholic fermentation : the type
of fermentation in which ethyl alcohol is the main end product .This
is very common in yeast (unicellular fungus) and also seen in some
bacteria. Yeast cells release enzymes called zymase complex
which bring about the fermentation. The reactions are similar to
anaerobic respiration.
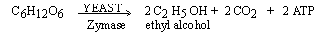
(2) Lactic acid fermentation : The type
of fermentation in which lactic acid is the end product.
It is carried out by some bacteria (e.g. lactic
acid bacteria), and also by animals (muscle glycolysis in animals,
under oxygen deficiency, results in the formation of lactic acid
this is whay we experience in muscle cramps, or "Charley horse").
Lactic acid bacteria can ferment milk sugar
lactose (C12H22O11) to lactic acid. The process is extracellular.
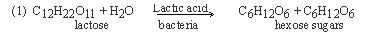
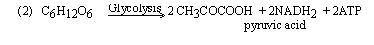
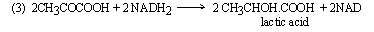
This brings about curdling of milk.
Commercial application of fermentation :
There are various kinds of fermentation carried on by different
microorganisms. Many of these result in highly useful end products.
Such useful microbial activity is used on large industrial scale
to obtain the useful end products for the benefit of mankind. Some
of the industrial products of the microbial fermentation activities
are (a) antibiotics (b) vitamins (c) industrial alcohol (d) bakery
products (e) some dairy products (f) tanning of leather (g) curing
of tea and coffee (g) lactic acid (h) butric acid, (i) acetic acid
etc.