All forms of life have one basic common requirement,
and that is energy. Energy gives the capacity to do work.
Organisms need energy for existence and maintenance of life. The
cell is the basic structural and functional unit of
an organism and it performs various metabolic and other vital activities.
These activities need energy, i.e. biologically usable forms of
chemical energy, such as the energy-rich organic compound called
ATP (adenosine tri-phosphate). ATP molecules act as energy
mediators in cells. For example, ATP undergoes a breakdown (hydrolysis)
and provides energy for energy requiring reactions. On the other
hand, ATP is synthesized by input of energy made available through
some energy-yielding reactions in the cell.
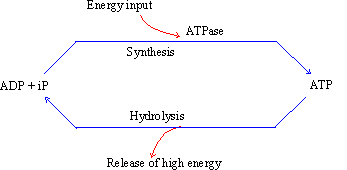
Figure 5
The solar energy that is trapped by green plants
is converted into chemical energy during photosynthesis and is stored
as food energy in carbohydrates and other organic food materials
(e.g. fats, oils, organic acids, proteins, etc.)
In cell metabolism, these energy-rich organic food
materials are oxidized and the stored energy is released as free
energy. This is utilized by the cell to perform various cellular
activities. Part of the energy is lost as heat.
In the cells, the process which supplies energy
through oxidation of organic compounds is called cellular respiration.
Definition : "Respiration is an intracellular
process of oxidation-reduction reactions in which the complex organic
food materials are broken down in a step-wise manner to form simpler
end products, with the release of energy and carbon dioxide."
It is basically an energy releasing and supplying
process. The energy released in respiration is of two types :
(a) Chemical energy, i.e. ATP. It is utilized
for the cellular activities.
(b) Heat energy. It is mostly lost. Depending
upon the availability of oxygen as an oxidant, respiration is of
two types : (1) aerobic respiration, in which oxygen in used
in the respiratory break down of organic substrate, and (2) anaerobic
respiration, in which oxygen is not used in the respiratory
breakdown of organic substrate.