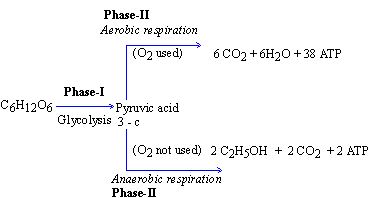
Respiration is of two types : aerobic and anaerobic
respiration.
(1) Aerobic respiration : "When
free or molecular oxygen participates in the respiratory breakdown
of organic substrate, it is called aerobic respiration." (In
this process, free molecular oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor.)
Aerobic respiration is represented by the following
chemical equation.
C6H12O6
+ 6O2 ® 6CO2
+ 6H2O + Energy
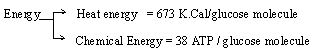
(2) Anaerobic respiration : "When
the respiratory breakdown of organic substrate takes place without
participation of free molecular oxygen, it is called anaerobic respiration."
(In this process, free or molecular oxygen is not the final electron
acceptor.)
Anaerobic respiration is represented by the
following chemical equation.
C6H12O6
® 2C2H5OH +
2CO2 + Energy
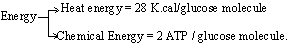
The process of respiration is completed in two
phases. Reactions in Phase I are called glycolysis and are
common to both types of respiration. Reactions in Phase II depend
upon whether O2 is utilized or not.