|
PinkMonkey Online Study Guide-Biology
10.3 Antibiotics
Definition : "An antibiotic is the complex
organic chemical substance which is produced as the secondary metabolite
by one micro-organism and acts as a toxin against other micro-organisms;
either inhibiting their growth or killing them."
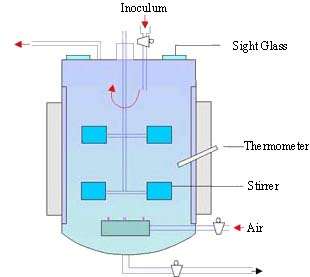
Figure 10.2 A stirred tank fermenter
Historical account : Penicillin was the first antibiotic to be produced industrially. The credit for the discovery of penicillin goes to Sir Alexander Fleming (1929). He extracted it from Penicillium notatum under laboratory conditions. However, the remarkable chemotherapeutic effectiveness of penicillin was demonstrated by Ernst B. Chain and Sir Howar W. Florey during 1939-41. Fleming, Chain and Florey shared the Nobel Prize in 1945 for their contributions in the field of antibiotics.
Selman Waksman (1942) coined the term "antibiotics".
He also discovered streptomycin.
Several thousand antibiotic substances have been discovered since then,
although only a few are of chemotherapeutic importance for the cure of
certain human diseases caused by bacteria, fungi and protozoa.
|
Table of Contents
10.0
- Introduction
10.1 Fermentation
10.2 Manufacture of Alcohol
10.3 Antibiotics
10.4 Vitamins
Chapter 11
|