|
Identities (formulas) for hyperbolic functions
Osborn's rule : In any formula connecting
the circular function of general angles, replace each circular function
by the corresponding hyperbolic function and change the sign of
every product (or square) of two sines directly or indirectly involving
in it and conversely.
Using this rule
e.g 1) 
2) 
Formulas
a) 1) cos h2x - sinh2x
= 1 2) sec h2x = 1- tan
h2x
3) cosec h2x
= 1 + cot h2x
b) 1) sin h (a
± b ) = sin ha
cos hb ± cos ha
sin hb
2)
cos h (a ± b
) = cos ha cos hb
± sin ha sin hb
3)
tan h ( a ± b
) = 

tan ha ± tan hb
1 ± tan ha tan hb
d) 1)
sin h2x = 2 sin hx cos hx
2) cos h2x = cos h2x + sin h2x
= 2 cos h2x-1
= 1 + 2 sin h2x
3)
tan h2x = 
e) 1)
cos h2x = 2) sin h2x =
2) sin h2x = 
f) 1) sin
h3x = 3 sin hx + 4 sin h3x 2)
cos h3x = 3 cos hx - 4 cos h3x
Inverse Hyperbolic Functions
If x = cos hy then we write y = cos h-1x
If x be real, we have

+ve value of the
R.H.S. is always taken.
Similarly it can be shown, if x is real

Differentiation and integration
(1) 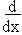 [
sin hx] = cos hx \
(1) ò cos hx dx = sin hx [
sin hx] = cos hx \
(1) ò cos hx dx = sin hx
(2) 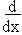 [cos hx] = sin hx \
(2) ò sin hx dx = cos hx
[cos hx] = sin hx \
(2) ò sin hx dx = cos hx
(3) 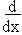 [ tan hx ] = sec h2x \
(3) ò sec h2x dx =
tan hx
[ tan hx ] = sec h2x \
(3) ò sec h2x dx =
tan hx
(4) 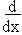 
\ (4) ò

(5) 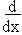 
(5) ò 
(6) 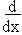
 =
=
\ (6) ò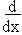 =
= 
(7) 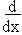 = =

\ (7) ò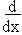 =
=
(8) 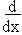
 = \ (8) ò
= \ (8) ò
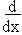 =
= 
[next page]
|