|
Example 6 Prove that
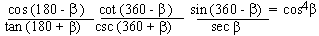
Solution
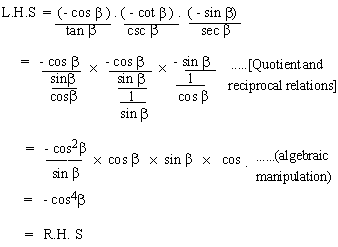
Example 7 Write sin
2340 in the form cos b, 0
< b< 900
Solution sin 2340
= sin ( 1800 + 540 )
= - sin 54 0 . . . . [sin (18
0 +  ) = - sin ) = - sin
 ] ]
= - sin (900 - 540) . .
. . [sin  = cos (900- = cos (900-
 )] )]
= - cos 360
Example 8 Show that cos b
cos (a - b)
- sin b sin ( a - b
) = cos a
Solution
L.H.S = cos b cos (
a - b ) -
sin b sin ( a
- b )
= cos [ b + ( a
- b ) ]
= cos a
= R.H.S.
Example 9
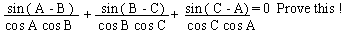
Solution
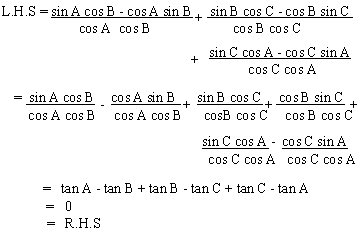
Example 10
Prove that 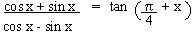
Solution
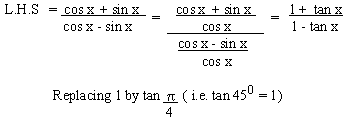
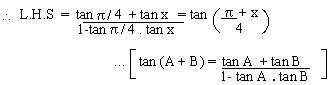
Example 11
Prove that 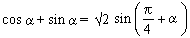
Solution
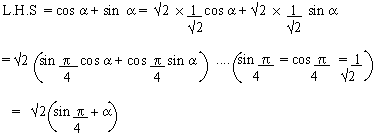
Example 12
If tan 250 = a 
Solution:
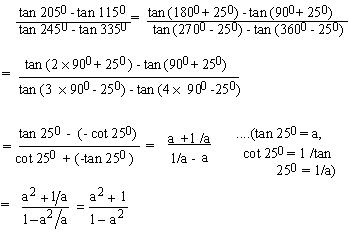
Example 13 Prove that 
Solution:
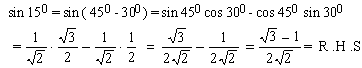
EXAMPLE 14 Prove that sin 190+
cos 190 = tan (640)
cos 190 - sin 190
Solution :
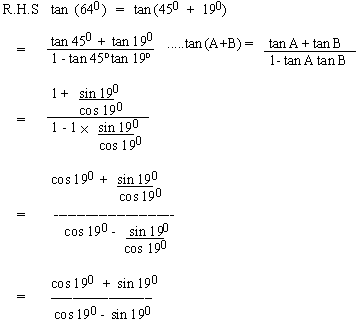
EXAMPLE 15 Find sin (a
+ b) if sin a
= - 4/5, cos b = 15/ 17 and a
and b are in Quadrant IV. Also state
the Quadrant of (a + b).
Solution
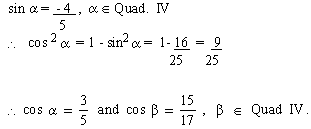
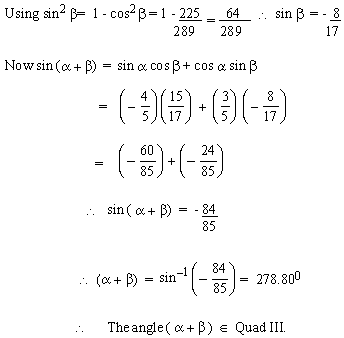
Example 16
If sin A = 5/13 and cos B = - 4 / 5. Find cos (A
+ B). State the Quadrant of (A + B) where A and B are obtuse angles.
Solution
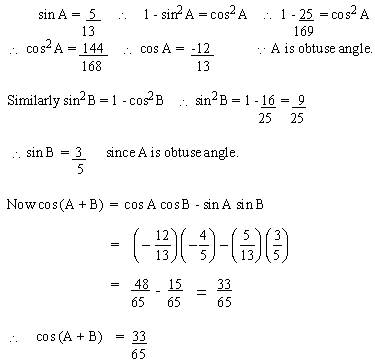
Since cosine ratio is +ve, the terminal arm of
(A+ B) lies in Quad IV.
Double - Angle
From the sum and difference formulas for sine and
cosine, one can get `double angle' formulas as :-
- sin 2q = sin (q
+ q)
= sin q cos q
+ cos q sin q
= 2 sin q cos q
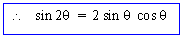
- cos 2q = cos (q
+ q)
= cos q cos q
- sin q sin q
= cos2q - sin2q
.....(1)

using Pythagorean identity sin2 q
= 1- cos2 q in (1)
\ cos 2 q
= cos2 q - (1- cos2q)
= 2cos2q - 1
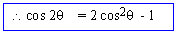
Also using cos2q
= 1 - sin2q in
(1)
cos 2q = 1 - sin 2 q
- sin2q
= 1 - 2 sin2q
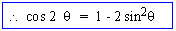
Trigonometric Ratios of (3a)
- sin 3a = sin (2a
+ a)
= sin 2a cos a
+ cos 2a sin a
= (2 sin a cos a)
cos a + (1 - 2sin2 a)
sin a
= 2 sin a cos2a
+ sin a - 2 sin3a
= 2 sin a (1- sin 2 a)
+ sin a - 2sin3a
= 2 sin a - 2 sin 3 a
+ sin a - 2 sin3a
= 3 sin a - 4 sin 3 a
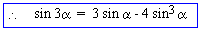
- cos 3a = cos (2a
+ a)
= cos 2a cos a
- sin 2a sin a
= (2 cos2 a - 1) cos a
- (2 sin a cos a)
sin a
= 2 cos3 a - cos a
- 2 sin2a cos a
= 2 cos3 a - cos a
- 2 (1 - cos2a) cos a
= 2 cos3a - cos a
- 2 cos a + 2 cos3a
= 4 cos3a - 3 cos a

[next page]
|