|
PinkMonkey Online Study Guide-Biology
During self-fertilization or inbreeding of the F1
dihybrids to produce an F2 generation, these male
and female gametes can form maximum to dihybrid unions as shown in the
Punnet’s Checker-board (Figure 7.3). These can be grouped into
four kinds on the basis of phenotypic appearance. i.e. yellow round,
yellow wrinkled, green round and green wrinkled in the ratio
of 9:3:3:1 respectively. This is called the Phenotypic dihybrid ratio.
In Figure 7.3, the 16 squares of the checker board are serially numbered for convenience. The squares represent the 16 possible combinations of the gametes which might result. The genotypes and the phenotypes of the F2 offspring are shown in the sixteen squares. A count of these squares shows the four kinds of phenotypes and their ratio in the F2 generation.
|
Phenotypes |
Square numbers |
|
Total |
|
Yellow Round |
1,2,3,4,5,7,9,10,13 |
... |
9 |
|
Yellow Wrinkled |
6,8,14 |
... |
3 |
|
Green Round |
11,12,15 |
... |
3 |
|
Green Wrinkled |
16 |
... |
1 |
In the actual dihybrid cross of the above type, Mendel obtained a total of 556 seeds in the F2 generation. The actual number of seeds of each type was as follows.
|
Phenotype |
Actual number obtained |
|
Yellow Round (Parental Combination) |
315/556 |
|
Yellow Wrinkled (New Combination) |
108/556 |
|
Green Round (New Combination) |
101/556 |
|
Green Wrinkled (Parental Combination) |
32/556 |
This gives approximately 9:3:3:1 ratio. Thus the actual results
agree completely with the theoretical expectations.
Method of calculating inheritance of each individual character (gene)
Multiplication rule states that the probability of two or more independent events occurring together is the product of their individual probabilities.
In the above mentioned dihybrid cross, the gene for shape
(round/wrinkled) and the gene for color (yellow/green)
are present together but are sorted independently (law of independent
assortment).
Calculation of F2 phenotypes in a dihybrid cross
The multiplication rule applies to the probabilities of the phenotypes. For each gene, the monohybrid phenotypic ratio is 3:1 or ¾ : ¼
Thus, for the color gene the monohybrid phenotypic the
ratio is 3 yellow : 1 green or ¾ yellow : ¼
green. And, for the shape gene, it is 3 Round :1 wrinkled
or ¾ Round : ¼ wrinkled.
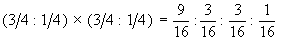
Therefore, in the dihybrid cross, the total probability of the
F1 phenotypes will be the product
of the two monohybrid ratios.
This is calculated as follows:
Gene for Gene
for Probabilities
shape color
of
Phenotypes
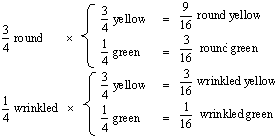
|