|
PinkMonkey Online Study Guide-Biology
6.3 Meiosis
In the sexually reproducing organisms, two important
phenomena regulate the number of chromosomes in the life cycle. These
are meiosis and fertilization. Meiosis is the reduction
division in which the diploid (2n) number of chromosomes is
reduced to haploid (n) during gamete formation (or spore formation).
Whereas, in fertilization, the two haploid gametes fuse to form
a diploid zygote. In this way, the diploid condition is restored
again in the life cycle.
 Click here to enlarge
Click here to enlarge
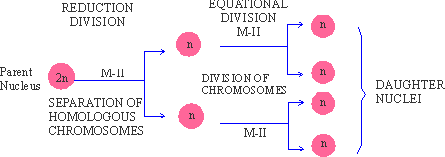
Figure 6.4 Meiosis-I (M-I, First meiotic division)
Definition : "Meiosis is a special type
of division characteristic of reproductive cells in which the diploid
number of chromosomes is reduced to haploid in the daughter cells.
In meiosis, chromosomes divide once while the nucleus (and in some
cases the cytoplasm also) divides twice. Four haploid daughter cells
result from one diploid mother cell. These differ from each other
as well as from the mother cell."
Homologous chromosomes : Sexually reproducing
diploid organism develops from a diploid zygote (2n). The zygote
is formed when haploid (n) male and haploid (n) female gametes
fuse at the time of fertilization. Thus, the diploid individual
receives two sets of chromosomes; one through the male gamete (paternal
set) and the other through the female gamete (maternal set).
For every chromosome in the paternal set, there is a similar looking chromosome
present in the maternal set. Such similar chromosomes from paternal and
maternal sets called homologous chromosomes. In this way, in both
the sets, all chromosomes have their homologues.
The meiotic cell cycle : It consists of the interphase, karyokinesis and cytokinesis.
Interphase : It consists of G1, S and G2 phases and involves changes as described earlier in this chapter.
The interphase nucleus : The nucleus enlarges
during interphase. The chromosomes are not clearly visible being very
thin and long threads. However, nucleus envelope and the nuclear are prominent.
Karyokinesis in meiosis : It consists of two complete nuclear divisions : Meiosis-I and Meiosis-II. The time interval between M-I and M-II is called interkinesis.
It is a reduction division during which a diploid
nucleus divides into two haploid nuclei through separation of homologous
chromosomes. Chromosomes are not duplicated in M-I.
|