|
PinkMonkey Online Study Guide-Biology
24.2 Female Reproductive cycle
The Menstrual Cycle
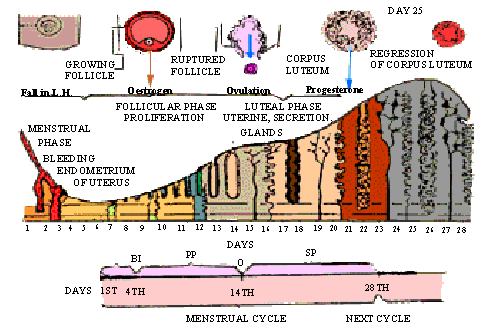
click here for enlargement
MENSTRUAL CYCLE
Figure 24.6 Menstrual cycle
From puberty (menarche-onset of the menses)
until menopause a womanís reproductive system undergoes many cyclic
changes are related to the changes in the endometrium (inner
lining of the uterus), breasts, ovaries, vagina, and hormone secretions.
The cyclic reproductive changes of the human female
is marked by menstruation, during which some cells, unclotted
blood from ruptured blood vessels, other fluids and the uterine
endometrium is released through the cervix and vagina. Each menstrual
cycle occurs about every 28 days and lasts 4-5 days. The menstruation
occurs 12 to 14 days after an ovum is released from the ovary (ovulation),
about once in four weeks. The periodicity of the cycle varies with
different individuals. After fertilization, menstruation ceases,
and is the first indication of pregnancy.
The menstrual cycle (of 28 days) is generally divided
into four phases, with major events occurring in each phase. The
4 phases are:
(1) The menstrual (destructive) phase,
(2) The proliferative (follicular) phase,
(3) The ovulatory phase, and
(4) The secretory (luteal) phase
1) The menstrual phase. The uterus lining (i.e.,
endometrium) and its blood vessels slough off , and is discharged with
blood, mucus, cell debris and other fluid as the menses , through
the vagina. This may last for 4-5 days. Menses occur when fertilization
does not take place.
2) The proliferative phase occurs between the
end of menses, and ovulation. In this phase, under the stimulation of
estrogen, the uterine endometrium undergoes a process of growth (proliferation)
and a new thick endometrium is formed. In the ovary, the follicle begins
to develop into a Graafian follicle. This phase cycle days 6 to 13 or
14 in a 28 day cycle.
3) The ovulatory phase indicates the rupture of the Graafian follicle and release of the ovum (ovulation). It occurs some 14 days after the start of menstruation. During this phase the concentration of estrogen is high in blood and it stimulates the ovulation. The blood vessels enlarge and grow in the endometrial wall, and some secretory cells or glands are formed.
(4) The secretory phase occurs between ovulation and the onset of menses, i.e., the phase lasts about 14 days (cycle days 15 to 28). The endometrium which is under the influence of progesterone and estrogen, increases in size, becomes thick, the endometrial glands become enlarged, undergo maximum secretory activity and its blood vessels become coiled and enlarged.
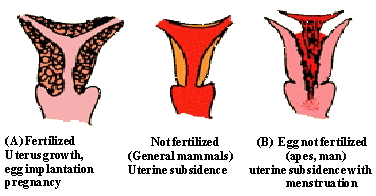
Mammalian uterus
[next page]
|
Table of Contents
24.0 Introduction
24.1 Human reproduction
24.2 Female reproductive cycle
24.3 Embryonic Development
Chapter 25
|