|
PinkMonkey Online Study Guide-Biology
19.3 Skin and Lungs as Accessory Excretory Organs
In addition to the urinary system, the skin, lungs and liver of vertebrates are accessory excretory organs.
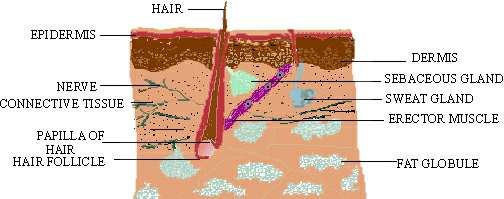
(1) Skin: Human skin possesses glands for secreting
two fluids on its surface, namely sweat from the sweat glands
and sebum from sebaceous glands. (Fig. 19.7). Sweat is a
watery fluid containing in solution primarily contains sodium-chloride,
lactic acid, urea, amino acids and glucose. It helps in excreting mainly
water and sodium chloride, and a small amount of urea and lactic acid.
 Click here to enlarge
Click here to enlarge
Figure 19.7 Vertical Section of the Skin
Sebum is a wax-like secretion which helps to excrete some lipids such as waxes, sterols, other hydrocarbons and fatty acids on the skin.
(B) Lungs: Lungs which are the main respiratory organs of vertebrates, help to eliminate the entire volume of carbon dioxide produced in the body, as well as some moisture, during expiration. The lungs maintain the blood-gas homeostasis through elimination of carbon dioxide. When lungs fail to eliminate enough carbon dioxide, the kidneys attempt to compensate. They change some of the carbon dioxide into sodium bicarbonate, which becomes part of the blood buffer system.
|
SUMMARY
(1) Excretion is the removal of nitrogenous
waste products from the body. (2) Animals are classified as
ammoniotelic, ureotylic, uricotylic and guanotelic according to
the predominant excretory product excreted. (3) Kidneys are the
most important excretory organs of mammals. Through filtration,
reabsorption and active transport, waste is remove, but kidneys
conserve substances useful to the organisms. (4) In general, kidneys
regulate the intake and the outflow of water and salts in the
blood and help to maintain homeostasis. (5) Regulation of kidney
function is achieved by certain hormones such as antidiuretic
hormone, aldosterone and angiotensin. (6) Skin and lungs also
act as accessory excretory organs.
|
**********
|
Table of Contents
19.0 -
Introduction
19.1 -
Ammonotelism, Ureotelism and Uricotelism
19.2 -
Excretory System of Man
19.3 -
Skin and Lungs as Accessory Excretory Organs
Chapter
20
|