|
PinkMonkey Online Study Guide-Biology
The mycelium is made up of profusely branched, septate,
multinucleated interwoven hyphae. The major part of the myceluim is underground
as in mushrooms, while in parasitic fungi like rusts and smuts it is in
the host. Some fungi like mushrooms produce an aerial fruiting body called
a basidiocarp made up of stalk and cap bearing gills on the under-surface.
Gills produce basidia giving rise to basidiospores, while some parasitic
fungi like rusts and smuts produce more than one type of spores in addition
to basidiospores outside the host. (Figure 14.46)
Reproduction : Asexual reproduction is uncommon. Sexual
reproduction takes place by the formation of basidiospores which are produced
by basidia exogenously.
Economic importance : Some mushrooms are used
as food for their delicacy and high nutritive value. Some basidiomycetes
are used as a source of medicinal compounds. Some are also used for "recreational"
purposes. Some like rusts and smuts cause destruction of crop plants.

Figure 14.48 Aspergillus
Dikaryotization in Ascomycetes and Basidiomycetes
Sexual reproduction takes place by the hyphae of two
opposite strains growing together in which their cytoplasms intermingles
(plasmogamy). Within this fused structure the nuclei of two different
strains come together in pairs, but they do not fuse. This is called dikaryotization.
Dikaryotic condition continues for a considerable period of time. New
hyphae develop from these fused structures and are called dikaryotic hyphae.
These hyphae form a fruiting body called an ascocarp or basidiocarp, characteristic
of the class.
Deuteromyucetes
They are also called imperfect fungi because of
their imperfect life-cycle, the sexual stage being undescribed. These
fungi reproduce asexually,( i.e. by means of conidia) and are closely
related to Ascomycetes, while a few are related to Basidiomycetes. Like
higher fungi the mycelium is made up of branched, multinucleated, septate,
interwoven hyphae. Some of the hyphae penetrate the substratum to absorb
nourishment,. while some aerial hyphae are called conidiophores. The latter
produce conidia which further give rise to mycelia.
Examples of imperfect fungi are Aspergillas and
Helminthosporium.
Economic importance : The fungus Penicillium
is used for the production of antibiotic penicillin. A few species
are used to give flavor and texture to cheese. Some are also commercially
used for the preparation of organic acid like citric acid, fumaric acid,
oxalic acid, etc. Some members cause ring worm and athlete's foot. Some
cause diseases in plants.
|
Ascomycetes and basidiomycetes are economically
important fungi. Some of them are used in various industries while
other are distinctly destructive. Yeast is used widely by brewers
and bakers to prepare alcohol and in raising bread. It is also the
main source of vitamin B and hormones like cytokinins. Some mushrooms
are used as food for their delicacy and high nutritive value. Fungi
like rusts and smuts cause destruction of crop plants while many
other cause spoilage of milk, eggs, meat, fish, vegetables, fruit,
etc.
|
3. Decomposers and parasitic forms
Decomposers
These serve as an important component of the ecosystem.
They release hydrolytic enzymes into the substratum and break down the
complex organic compound into simpler ones, release minerals and make
them available to plants for recycling.
Examples: Rhizopus, Mucor, Agaricus,
Penicillium, If it was not for the actions of decomposers, nutrients
would get locked up in the dead matter of organisms. Life on earth without
these organisms eventually would become impossible.
Role of decomposers
(1) They decompose the dead matter of plants and animals
and disperse their nutrients, thus acting as scavangers of nature.
(2) They help in the formation of humus (superficial layer of soil rich in organic compounds) which is important to increase the fertility of soil and healthy growth of plants.
(3) They play an important role in converting complex organic components into simple forms to continue biogeochemical cycles.
Parasitic forms
These are pathogenic fungi. Unlike saprophytes or decomposers,
they do not secrete hydrolytic enzymes, They live on or inside the body
of the other living organisms (called hosts) obtain ready-made
food from the latter and produce a number of diseases in them. Common
plant diseases are potato blight, wheat rust (Figure 14.45) corn smut,
and powdery mildew.
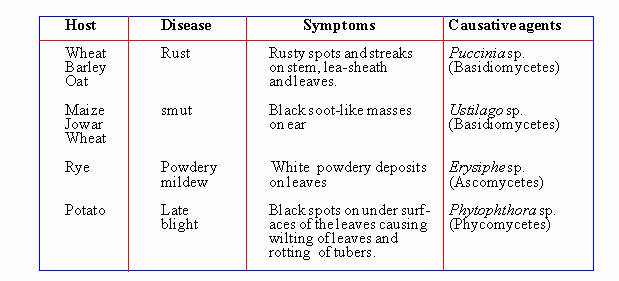
Click here to enlarge
|