|
PinkMonkey Online Study Guide-Biology
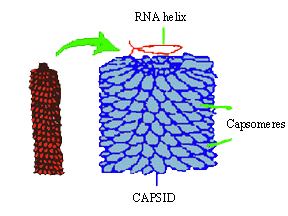
Figure 14.3 Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV)
(plant virus)
Classification of viruses : According to the type
of hosts they infect, viruses may be classified as one of the following
three types:
(i) Plant viruses: These are pathogenic viruses
which infect plants. They are usually rod-shaped, containing nucleic acid
in the form of RNA, e.g. tobacco mosaic virus (TMV), beet yellow virus
(BYV) etc. The capsomeres of TMV virus are elliptical and arranged helically
around the central nucleic acid core (fig. 14.3).
Common plant viral diseases are (a) mosaic disease of
tobacco, papaya, apple etc., (b)black ring spot of cabbage, (c) leaf-roll
of potato, and (d) spotted wilt of tomato.
(ii) Animal viruses: These are pathogenic viruses infecting
animals. They are generally polyhedral or spherical in shape. The capsid
in some is surrounded by envelope, and the nucleic acid is either DNA
or RNA.
According to the type of tissue which they infect, they are as follows:
(a) Dermatotropic: Viruses infecting the skin, e.g. measles, chicken pox.
(b) Viscerotropic: Viruses infecting viscera, e.g.
yellow fever, jaundice, mumps.
(c) Neurotropic: Viruses infecting nervous system,
i.e. polio, meningitis.
(iii) Bacterial virus: These are pathogenic viruses
infecting bacteria and are called bacteriophages or simply phages.
their nucleic acid is DNA, e.g. T2, T4, T6 bacteriophages.
Significance
1. Viruses are a kind of biological puzzle to biologists as they are at the threshold of living and non-living, showing the characteristics of both.
2. Viruses are used by humans in eradicating harmful
pests like insects and in controlling the population of organisms such
as rabbits by inducing viral infection. Thus they are used as a
form of biological control.
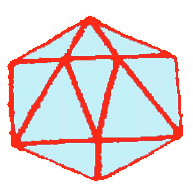
Figure 14.4. Adenovirus (animal virus)
3. Viruses have gained a prominent position in world because
of their value as biological research tools. Due to simplicity
of structure and rapid multiplication, they are widely used in research,
in the fields of molecular biology, medicine and genetic engineering.
Their role in fundamental research to unlock the intricate phenomena of
life, can never be over- emphasized.
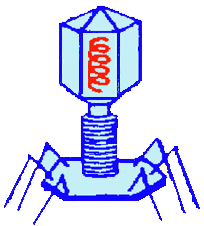
Figure 14.5 Bacteriophage ( bacterial virus )
4. Viruses have also concerned agriculturists. Apart
from causing diseases in crops, bacteriophages attack the nitrogen
fixing bacteria of the soil and are responsible for reducing fertility
of the soil.
5. In industry, however, viruses are used in preparation of sera and vaccines to be used against diseases like rabies, polio, etc. The multiplication of viruses in bacterial cell is also utilized in the production of antibodies.
|