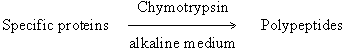
(iii) Amylopsin: It is a pancreatic amylase
which acts on starch and complex sugars as follows:
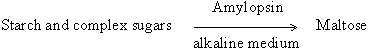
(iv) Steapsin: It is a pancreatic lipase
acting on emulsified fats as follows:
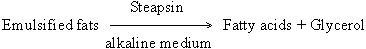
(C) Action of Intestinal juice (saccus entericus):
It contains the enzyme erepsin which is mainly a group of
peptidases. It also contains traces of maltase, sucrase, lactase
and lipase.
(i) Peptidases are the intestinal
proteases acting on peptides as follows:

(ii) Maltase is an intestinal
amylase, acting as follows:
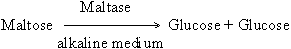
(iii) Sucrase acts on cane
sugar as follows:

(iv) Lactase acts on the milk sugar
lactose, as follows:

(v) Lipase acts on emulsified fats
as follows:
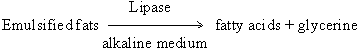
By this time, the food is completely digested and
converted into a liquid form called chyle which is further
subjected to absorption in the small intestine.
The large intestine has no digestive function.
It absorbs water from the undigested matter. which is further acted
upon by bacteria which live permanently in the colon of the large
intestine as symbionts. An appreciable quantity of vitamins is obtained
due to activities of these bacteria. The rectum absorbs these vitamins
and water, and then drives out the solid residue or feces through
the anus. This process is called egestion.