|
PinkMonkey Online Study Guide-World History
17.4 The Cold War between 1953 and 1963
During this phase of the cold war, the US continued
her policy of military and economic offensive. On September 8, 1954,
the Treaty of Collective Defense of South-East Asia, known
as SEATO was signed by the US, Great Britain, France, New
Zealand, Pakistan, Thailand and the Philippines, for the collective
defense for preserving peace and security in the "treaty area."
The Baghdad Pact which was signed in 1955
between Iraq and Turkey, had military and economic aspects. Britain,
Pakistan and the US entered into the Pact later. It was directed
not only against the Soviet Union, but also against the non-aligned
Arab states.
On May 19, 1954, the Mutual Defense Assistance
Agreement was signed between the governments of Pakistan and
the US
The Warsaw Pact was the Treaty of Friendship,
co-operation and Mutual Assistance signed by Albania, Bulgaria,
Hungary, Czechoslovakia, East Germany, Poland, Rumania and the Soviet
Union in May 1955, in order to meet the challenge from the US and
her allies.
Indo-China was a troubled area after World War
II. After the Geneva Agreements were signed, Vietnam was
partitioned so that North Vietnam was to be under the Communists,
and South Vietnam was to be under the French. However, the whole
of South Vietnam fell into the hands of the Communists in April
1975. The cold war in Indo-China ended in the complete victory of
the Soviet Union and Communist China, against the US and her allies.

Exhibit 17.4
The USSR and US leaders battle it out during the Cold War
The Cuban Crisis
Thanks to Cuba, Latin America obtained a
first-hand experience of the cold war.
Cold War in Africa
In Africa, the Soviet Union helped the Congo in
order to balance the influence of the Western powers.
The Suez Canal crisis in 1956 after
the Suez Canal was nationalized by President Nasser of Egypt. In
a bid to re-exert international control over the canal, Israeli
forces attacked Egyptian positions in the Suez Canal zone. Britain
and France joined the attack against Egypt. Eventually, the US put
pressure on Britain and France who withdrew their forces from Egypt.
This resulted in the resignation of British prime minister Eden.
The Australian prime minister, Robert Menzies was appointed to bring
about a settlement. However, his mission was unsuccessful. Besides
the military intervention in the whole affair met with Soviet protest.
America too did not support this. Hence US relations with Britain,
France and Australia were strained for a while.
The Eisenhower Doctrine was enunciated by
President Eisenhower for the Middle East, proclaiming the American
intention to use armed forces against any communist aggression in
the Middle East. The Eisenhower Doctrine aimed at providing economic
and military aid to any nation threatened by Communism.
The Partial Nuclear Test Ban Treaty was
signed on August 5, 1963 by the US, the Soviet Union and Great Britain.
It provided for a limited ban on nuclear tests in the atmosphere,
beyond its limits, including territorial waters or high seas.

Exhibit 17.5
The Cuban leader, Fidel Castro
Fidel Castro took over the reigns of the Cuban
government from January 1, 1959, after overthrowing the then leader
Fulgencio Batista. He went on to nationalize American-owned industrial
estates and companies and then struck a trade agreement with the
Soviet Union. This naturally led to a deterioration in US-Cuban
relations. The US broke off all ties with Cuba in 1961. After this,
with Kennedy’s backing the deposed Batista’s supporters invaded
Cuba, landing in the Bay of Pigs. The rebels were easily crushed
by the Cuban forces. This event resulted in Castro declaring himself
a Marxist and Cuba becoming communist.
It was found from aerial surveys that medium-range
ballistic missiles had been installed in Cuba. On October 22, 1962,
President Kennedy declared that there was to be a strict
quarantine on all offensive military equipment bound for Cuba. This
came into effect on October 24, 1962. Ultimately, the Soviet Union
agreed to dismantle the Cuban missile sites and transport the missiles
back to the Soviet Union. Thus the imminent danger of a world war
was averted, owing to the restraint shown by Khrushchev on this
occasion.
The Cuban crisis had several consequences, of which
the danger of a nuclear holocaust was the most significant.
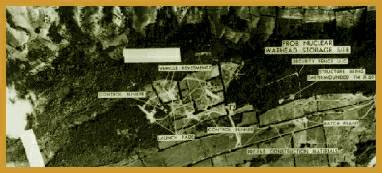
Exhibit 17.6
A Photograph of the Cuban missile site
[next page]
|