|
PinkMonkey Online Study Guide-World History
The fertile land of Mesopotamia was only a part of a narrow but
fertile strip of land which was called the ’Fertile Crescent.’
It was open to invasion by so many tribes that it became a melting
pot of cultures namely the Sumerian, the Babylonian,
the Assyrian, the Chaldean and a host of others. The
Sumerians who occupied the lower portion of the Tigris Euphrates
Valley, excelled in metal-works, gem-carving and sculpture.
Their weapons, vessels and jewelry had humans and animals carved on them. They were also excellent in the art of making seals that they used in trade and commerce, to indicate the identity of a merchant. The Babylonians or Amorites had a famous king Hammurabi who gave to his people and the world, the earliest code of laws. The Babylonians achieved great success in science. Their special field was astronomy. The Assyrians set up for the Persians an example in the management of a vast expire.
Secondly, Assyria established a military organization and built
an empire on its strength. This served as a lesson for the Romans
in later days. Thus the Assyrians influenced later-day cultures.
The Chaldeans made wonderful contributions in the field of astronomy.
They were the first to make this subject a methodical and systematized
science.
The Phoenicians, who occupied the narrow strip of land between Syria and the Mediterranean Sea, were carriers of cultures. They blended the cultures of Egypt and Babylonia, thus becoming a link between the East and the West.
The Hebrews made great contributions in the spiritual and ethical spheres. The two great religions of Judaism and Christianity are based upon their philosophy. Will Durant has rightly remarked, "the numerically and geographically insignificant Jews gave to the world one of its greatest literatures, two of its most influential religions, and so many of its profoundest men."
India also passed through the Stone Age, the Iron Age and the Copper Age. Paleolithic remains were found in the Deccan and Southern India, while Neolithic sites were found almost all over India.
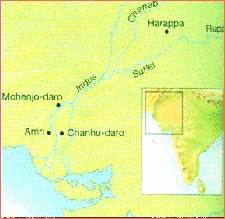
Exhibit 1.3
The main centers of the Indus Valley civilization
|