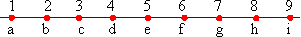
Since the letters represent consecutive integers, moving backwards from f to b
one gets 4 units.
\ f - b = 6 - 2 = 4
Ans : B
 Since the letters represent consecutive integers, the sum c + d + g = 3c + 5
Since the letters represent consecutive integers, the sum c + d + g = 3c + 5
\ c + d + g = c + c + 1 + c + 4
= 3c + 5
Ans : A

Since the letters represent consecutive integers, consider
b = a + 1, c = a + 2, and d = c + 1
To find d2 - b2
Substituting the values of d as (c + 1) and b as (a + 1)
(c + 1)2 - (a + 1)2 = c2 + 2c + 1 - a2 - 2a - 1
= c2 - a2 + 2 ( c - a)
= 24 + 2 ( c - a) [Since c2 - a2 = 24]
But c = a + 2
\ d2 - b2 = 28
Ans : E

Ans : C
[next page]