| PinkMonkey Study Guide - American History
8. 1 Woodrow Wilsonís Administration
Tariffs
The first reform legislation made by the Democrat President on assuming office was to reduce tariffs. A special session of the Congress was summoned to revise the tariffs. Consequently on October 3rd 1915, the Underwood-Simmons Bill was prepared which laid down the lowest tariffs since the Civil War. The Bill also provided for an income tax to make for the loss in tariff receipts.
The Federal Reserve System
The next in the series of Wilsonís reform program
was the control of banking and currency in the U.S. After the Panic
of 1907, the Pujo Committee (1912 ) revealed that a small
section of New York Bankers virtually control the entire nationís
economy. Several businessmen and politicians advocated the need
for a central Bank very similar to Hamiltonís concept. But the Wilson
government favored a decentralized banking system under a strong
federal jurisdiction. Therefore, after several months of debates,
the Congress adopted the Glass-Owen Bill in Dec 1913. This
Bill set up the Federal Reserve System. The Bill also divided the
nation into 12 administrative districts and established a Federal
Reserve Bank in each district. These banks were to serve as the
fiscal agent to the other bankers. The entire system was to be supervised
by a Central Federal Reserve Board of seven members. The Board included
the Secretary of the Treasury. Besides, the Bill made provisions
for a new currency known as Federal Reserve notes. This act
helped in better banking facilities in the western and southern
states.
The Anti-Trust Act
The third important legislative reform of Wilsonís administration was an attack on various industrial trusts. The Pujo Committee revealed that a movement towards monopolistic control in the field of industry, banking and corporation was on in the U.S. To check this unhealthy phenomenon, Wilson introduced the Sherman Anti-Trust Act (1914). This act declared a number of unfair business practices (that prevented competition in the market) as illegal. It should be noted that labor unions were exempted from the Anti-Trust laws. Section 20 of the Act restricted the use of injunctions in labor disputes and made it clear that strikes, boycotts and picketing were not opposed to any law.
Further to prevent any unfair methods of competition, to Congress in 1914 passed the Federal Trade Commission Act. This act set up a Federal Trade Commission of 5 members to be appointed by the President. If the commission found a business involved in illegal or unfair practices, it could issue cease and desist orders against it. The commission also made it necessary for all corporations to file certain information before starting business.
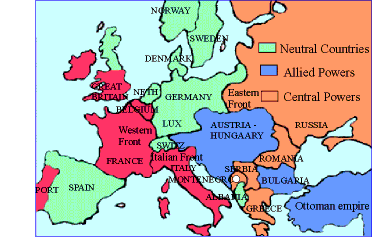
Exhibit 8.1
In 1914, Europe was divided into two fronts, an Eastern Front and a Western Front. There were a few neutral countries as well.
[Next Page]
|